Known issues Innovation Release
These are the currently known issues and limitations identified in the Hybrid Manager (HM) Innovation Releases. Workarounds can sometimes help you mitigate the impact of these issues. These issues are actively tracked and will be resolved in a future release.
Multi-DC
Multi-DC configuration loss after upgrade
Tip
Resolved in HM versions 2025.12 and later.
Description: Configurations applied by the multi-data center (DC) setup scripts (for cross-cluster communication) don't persist after an HM platform upgrade or operator reconciliation.
Workaround: After every HM upgrade or component reversion, run the multi-DC setup scripts again to reapply the necessary configurations.
Location dropdown list is empty for multi-DC setups
Tip
Resolved in HM versions 2025.12 and later.
Description: In multi-DC environments, the API call to retrieve available locations fails with a gRPC message size error (429/4.3MB limit exceeded). This is due to the large amount of image set information included in the API response, resulting in an empty location list in the HM console.
Workaround: This advanced workaround requires cluster administrator privileges to limit the amount of image set information being returned by the API. It involves modifying the image discovery tag rules in the upm-image-library and upm-beacon ConfigMaps, followed by restarting the related pods.
Workaround details
The workaround modifies the regular expressions (tag rules) used by the image library and HM agent components to temporarily limit the number of image tags being indexed. This reduces the API response size, allowing the locations to load.
Find the
upm-image-libraryConfigMap:kubectl get configmaps -n upm-image-library | grep upm-image-library # Example Output: upm-image-library-ttkt29fmf7 1 5d3h
Edit the ConfigMap and modify the
tagsrule under each image discovery rule (edb-postgres-advanced,edb-postgres-extended,postgresql). Replace the existing regex with the limiting regex:# Snippet of the YAML you will edit in the ConfigMap "imageDiscovery": { "rules": { "(^|.*/)edb-postgres-advanced$": { "readme": "EDB postgres advanced server", "tags": [ "^(?P<major>\\d+)\\.(?P<minor>\\d+)-2509(?P<day>\\d{2})(?P<hour>\\d{2})(?P<minute>\\d{2}) (?:-(?P<pgdFlavor>pgdx|pgds))?(?:-(?P<suffix>full))?$" ] }, # ... repeat for edb-postgres-extended and postgresql ... } }
Note
If you're running a multi-DC setup, perform this step on the primary HM cluster.
Restart the Image Library pod:
kubectl rollout restart deployment upm-image-library -n upm-image-libraryGet the
upm-beaconConfigMap to modify the HM agent configuration:kubectl get configmaps -n upm-beacon beacon-agent-k8s-configEdit the ConfigMap (
beacon-agent-k8s-config) and modify thetag_regexrule under eachpostgres_repositoriesentry (edb-postgres-advanced,edb-postgres-extended,postgresql).# Snippet of the YAML you will edit in the ConfigMap postgres_repositories: - name: edb-postgres-advanced description: EDB postgres advanced server tag_regex: "^(?P<major>\\d+)\\.(?P<minor>\\d+)-2509(?P<day>\\d{2})(?P<hour>\\d{2})(? P<minute>\\d{2})(?:-(?P<pgdFlavor>pgdx|pgds))?(?:-(?P<suffix>full))?$" # ... repeat for edb-postgres-extended and postgresql ...
Restart the HM agent pod:
kubectl rollout restart deployment -n upm-beacon upm-beacon-agent-k8s
After completing these steps, the reduced image data size allows the location API call to succeed and the locations to appear correctly in the HM console.
Dedicated object storage for project isolation
Tip
Resolved in HM versions 2025.12 and later.
Description: In the current iteration, project boundaries aren’t strictly applied, and authorized users on one project may have visibility of the data and databases of other projects. For this reason, granular project access is available for HM.
Workaround: Create dedicated object storage for new projects and enable project isolation.
Workaround details: If you need to isolate project resources, you can configure dedicated object storage for each project.
Core platform and resources
Cross-stream upgrade issues for OpenShift users
Description: Due to the OpenShift Operator Lifecycle Manager (OLM) enforcing strict semantic versioning, date-based versions (like 2026.1) are interpreted as being significantly "higher" than standard versions (like 1.4). This can prevent the OLM from recognizing a move to an LTS version as an upgrade.
Workaround: There is no workaround available for this issue. We are currently decoupling the Operator versions from the HM application versions to resolve this.
upm-beacon-agent memory limits are insufficient in complex environments
Description: In environments with many databases and backups, the default 1GB memory allocation for the upm-beacon-agent pod is insufficient, which can lead to frequent OOMKill or crashloop issues. This resource limit currently isn't configurable via the standard Helm values or HybridControlPlane CR.
Workaround: Manually patch the Kubernetes deployment to increase the memory resource limits for the upm-beacon-agent pod.
IdP configuration fails after upgrade to version 2026.02
Description: In some cases, upgrading from version 2026.01 to 2026.02 can cause your Identity Provider (IdP) configuration to display the Expiring Soon status in the HM console. This is caused by a race condition during the migration process. While this issue doesn't occur in every environment, it prevents users from successfully authenticating via their IdP provider if triggered.
Workaround: To resolve this state and allow the configuration to restore correctly, a cluster administrator must manually update the internal application database.
Execute the following SQL statement on the internal app-db database before attempting to re-setup the IdP integration in the HM console:
UPDATE upm_api_admin.idp SET deleted_at = NOW() WHERE deleted_at IS NULL;
accm-server fails to start due to missing Langflow secret
Description: The accm-server component currently has a hard dependency on a Kubernetes secret named langflow-secret. This secret is required even in installation scenarios where AI features aren't being used. If the secret doesn't exist, the accm-server pod will fail to start with the error CreateContainerConfigError.
Workaround: To allow the accm-server to start in environments where AI features aren't installed, you must manually create a placeholder secret in the upm-beaco-ff-base namespace.
You can create an empty secret using the following kubectl command:
kubectl create secret generic langflow-secret -n upm-beaco-ff-base --from-literal=LANGFLOW_NOT_INSTALLED=true
Once the secret exists, the accm-server pod will be able to mount the volume and transition to a Running state.
Database cluster engine
Failure to create 3-node PGD cluster when max_connections is non-default
Description: Creating a 3-data-node PGD cluster fails if the configuration parameter max_connections is set to a non-default value during initial cluster provisioning.
Workaround: Create the PGD 3-data-node cluster using the default max_connections value. Update the value after the cluster is successfully provisioned.
AHA witness node resources are over-provisioned
Description: For advanced high-availability (AHA) clusters with witness nodes, the witness node incorrectly inherits the CPU, memory, and disk configuration of the larger data nodes, leading to unnecessary resource over-provisioning.
Workaround: Manually update the pgdgroup YAML configuration to specify and configure the minimal resources needed by the witness node.
HA clusters use verify-ca instead of verify-full for streaming replication certificate authentication
Description: Replica clusters use the less strict verify-ca setting for streaming replication authentication instead of the recommended, most secure verify-full. This is currently necessary because the underlying CloudNativePG (CNP) clusters don't support IP subject alternative names (IP SANs), which are required for verify-full in certain environments (like GKE load balancers).
Workaround: None. A fix depends on the underlying CNP component supporting IP SANs.
Second node is too slow to join large HA clusters
Tip
Resolved in HM versions 2025.12 and later.
Description: For large clusters, the pg_basebackup process used by a second node (standby) to join an HA cluster is too slow. This can cause the standby node to fail to join, which prevents scaling a single node to HA. It also causes issues when restoring a cluster directly into an HA configuration.
Workaround: Avoid the best practice of loading data into a single node and then scaling to HA. Instead, load data directly into an HA cluster from the start. There's no workaround for restoring a large cluster into an HA configuration.
EDB Postgres Distributed (PGD) cluster with 2 data groups and 1 witness group not healthy
Description: PGD clusters provisioned with the topology of two data groups and one witness group may fail to reach a healthy state upon creation. This failure is caused by an underlying conflict between the bdr extension (used for replication) and the edb_wait_states extension. The combination of these two extensions in this particular topology prevents the cluster from initializing successfully.
Backup and recovery
Replica cluster creation fails when using volume snapshot recovery across regions
Tip
Resolved in HM versions 2025.12 and later.
Description: Creating a replica cluster in a second location that's in a different region fails with an InvalidSnapshot.NotFound error because volume snapshot recovery doesn't support cross-region restoration.
Workaround: Manually trigger a Barman backup from the primary cluster first. Then use that Barman backup (instead of the volume snapshot) to provision the cross-region replica cluster.
Volume snapshot restoration is limited to the same region
Description: While HM automatically handles cross-region data synchronization for replica clusters using the internal backup mechanism, manual restoration of a cluster from a volume snapshot doesn't support cross-region operations. If you attempt to restore a cluster to a location in a different region using a volume snapshot, the operation will fail because snapshots are geographically restricted to their source region.
Workaround: To restore data to a location in a different region, use a Barman backup instead of a volume snapshot. Barman backups are accessible across regions.
WAL archiving is slow due to default parallel configuration
Description: The default setting for wal.maxParallel is too restrictive, which slows down WAL archiving during heavy data loads. This can cause a backlog of ready-to-archive WAL files, potentially leading to disk-full conditions. This parameter isn't yet configurable on the HM console.
Workaround: Manually edit the objectstores.barmancloud.cnpg.io Kubernetes resource for the specific backup object store and increase the wal.maxParallel value (for example, to 20) to accelerate archiving.
transporter-db disaster recovery (DR) process may fail due to WAL gaps
Description: The DR process for the internal transporter-db service may fail when restoring from the latest available backup. This occurs in low-activity scenarios where a backup was completed, but no subsequent write-ahead log (WAL) file was archived immediately following that backup. This gap prevents the restore process from successfully completing a reliable point-in-time recovery.
Workaround: To ensure a successful restore, select an older backup to restore that has at least one archived WAL file immediately following it. This makes the needed transactional logs available for the recovery process.
AI Factory and model management
Failure to deploy nim-nvidia-nvclip model with profile cache
Description: Model creation for the nim-nvidia-nvclip model fails in the AI Factory when the profile cache is used during the deployment process.
Workaround: An administrator must manually download the necessary model profile from the NVIDIA registry to a local machine. They must then upload the profile files directly to HM's object storage path. Then they deploy the model by patching the Kubernetes InferenceService YAML with a specific environment variable to force it to use the pre-cached files instead of attempting a failed network download.
Workaround details
Log in to the NVIDIA Container Registry (nvcr.io) using your NGC API key:
docker login nvcr.io -u '$oauthtoken' -p $NGC_API_KEY
Pull the Docker image to your local machine:
docker pull nvcr.io/nim/nvidia/nvclip:latestPrepare a local directory for the downloaded profiles:
mkdir -p ./model-cache chmod -R a+w ./model-cache
Select the profile for your target GPU.
For example, A100 GPU profile:
9367a7048d21c405768203724f863e116d9aeb71d4847fca004930b9b9584bb6Run the container to download the profile. The container is run in CPU-only mode (
NIM\_CPU\_ONLY=1) to prevent GPU-specific initialization issues on the download machine.export NIM_MANIFEST_PROFILE=9367a7048d21c405768203724f863e116d9aeb71d4847fca004930b9b9584bb6 export NIM_CPU_ONLY=1 docker run -v ./model-cache:/opt/nim/.cache -u $(id -u) -e NGC_API_KEY -e NIM_CPU_ONLY -e NIM_MANIFEST_PROFILE --rm nvcr.io/nim/nvidia/nvclip:latest
This container doesn't exit. You must manually stop the run (Ctrl+C) after you see the line
Health method calledin the logs, which confirms the profile download is complete.Upload the profiles from your local machine to the object storage bucket used by your HM deployment:
gcloud storage cp -r ./model-cache gs://uat-gke-edb-object-storage/model-cache/nim-nvidia-nvclip
Note
Adjust the
gs://path to match your deployment's configured object storage location.Create the model
nim-nvidia-nvclipusing the HM console, specifying the Model Profiles Path field as the previous location (for example,/model-cache/nim-nvidia-nvclip). The deployment will initially fail or become stuck.Export the InferenceService YAML from the HM Kubernetes cluster.
Add the necessary environment variable,
NIM_IGNORE_MODEL_DOWNLOAD_FAIL, to the env section of thespec.predictor.modelblock in the exported YAML. This flag tells the NIM container to use the locally available cache (the files you uploaded) and ignore the network download failure.# --- Snippet of the modified InferenceService YAML --- spec: predictor: minReplicas: 1 model: modelFormat: name: nim-nvidia-nvclip name: "" env: - name: NIM_IGNORE_MODEL_DOWNLOAD_FAIL # <-- ADD THIS LINE value: "1" # <-- ADD THIS LINE resources: # ... resource requests/limits ... runtime: nim-nvidia-nvclip storageUri: gs://uat-gke-edb-object-storage/model-cache/nim-nvidia-nvclip # ---------------------------------------------------
Apply the modified YAML using kubectl to force the deployment to use the pre-downloaded profiles:
kubectl apply -f <modified-inference-service-file.yaml> -n <model-cluster-namespace>
The pods now start successfully, using the model profiles you manually provided using object storage.
AI Model cluster deployment stalls if object storage path for model profiles is empty
Tip
Resolved in HM versions 2025.11 and later.
Description: Creating an AI Model cluster and specifying an object storage path in the Model Profiles Path field causes the deployment to stall at the pending stage. This issue occurs if the specified path contains no content (that is, the model profile doesn't yet exist).
Workaround: Ensure that the object storage path specified in the Model Profiles Path field contains a correct, valid profile before initiating the model cluster deployment.
Model configuration settings reset after Innovation Release upgrade
Description: After upgrading HM from the 2025.11 to the 2025.12 Innovation Release, the existing model configuration settings are unintentionally reset to empty. This results in a model_not_found error, preventing access to AI services and causing issues like knowledge bases (KBs) failing to display in the HM console.
Workaround: In the HM console, manually reenter or set your required model configurations to restore functionality.
Error page appears when editing knowledge base credentials
Description: When editing a knowledge base (KB) that was created from a pipeline in the HM console, skipping the username field and immediately navigating to the password field triggers a client-side JavaScript error (Cannot read properties of null), which results in an Unexpected Application Error! page.
Workaround: To prevent the error page from appearing, fill in the Username field immediately after selecting Edit KB and before attempting to enter the password.
Missing aidb_users role on PGD witness node prevents AI functionality
Description: The aidb_users role (necessary for AI Factory functionality) and its related extension aren't being successfully replicated to the witness node of a PGD cluster during cluster initialization. This issue is specific to PGD clusters that use a single witness node (as opposed to a witness group) and results in the AI Factory encountering errors due to the missing required role.
Workaround: To manually install the necessary role and allow the AI Factory to function, execute the following SQL commands directly on the PGD witness node:
begin; set local bdr.ddl_replication = off; SET LOCAL bdr.commit_scope = 'local'; create user aidb_users; commit;
GenAI Builder structures and tools execution failure
Tip
Resolved in HM versions 2025.12 and later.
Description: GenAI Builder's structures and tools capabilities don't function correctly unless specific environment variables are configured during their creation. If these variables are missing or incorrect, execution fails with the following error:
[Errno -2] (Name or service not known)
Workaround: When creating a structure in GenAI Builder, set the following environment variables in the Create Structure panel:
GT_CLOUD_BASE_URL: Must be set to the full project path:https://<PORTAL URL>/apps/genai-builder/projects/<PROJECT ID>REQUESTS_CA_BUNDLE: Must be set to the following certificate path:/etc/ssl/certs/hcp.crt
Screenshot of variables
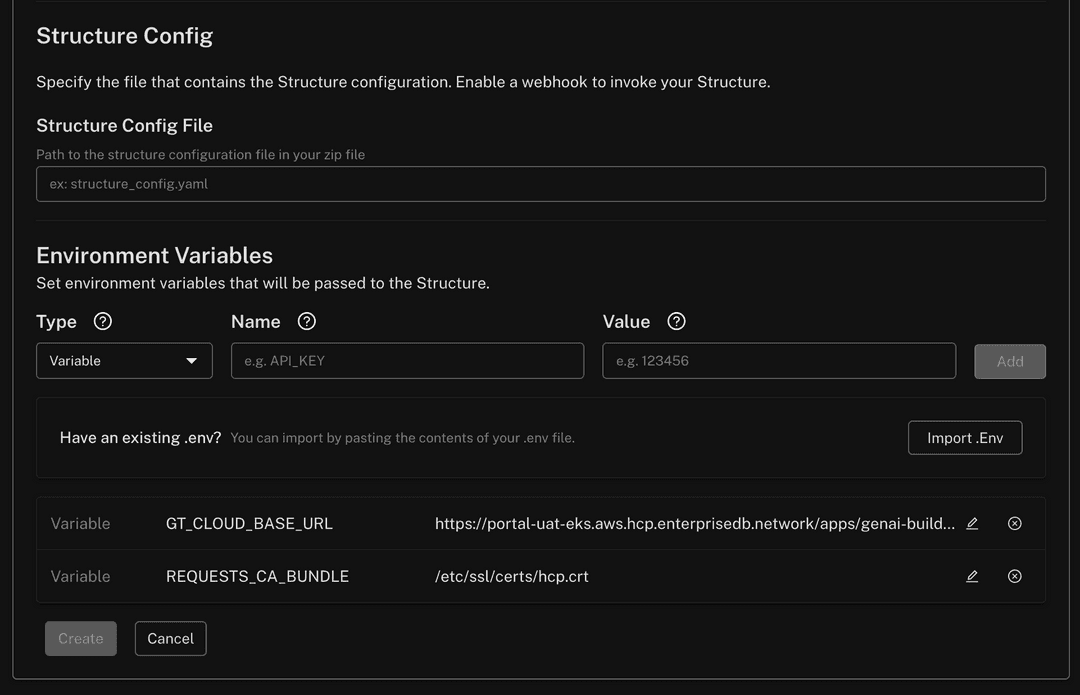
Pipeline Designer-created knowledge bases not visible to GenAI Builder
Description: In HM 2025.12, knowledge bases (KBs) created with Pipeline Designer (PD) are assigned to the visual_pipeline_user role.
This is done to enforce strict isolation, ensuring HM users can't access SQL-created KBs (and vice versa) by default.
However, this isolation prevents GenAI Builder from querying these KBs out of the box.
Workaround: Explicitly share PD-created KBs with your specific PostgreSQL user account to make them queryable in GenAI Builder.
Workaround details
Example scenario
Alice connects to HM as alice@acme.org and to PostgreSQL as the database user alice. She must share the PD KBs with the alice database user to enable GenAI Builder agents to query them using her credentials.
Prerequisite: Ensure user existence
Ensure the target PostgreSQL user (
alicein this example) exists and is assigned theaidb_usersrole. If the user doesn't exist, execute the following (assuming EDB documentation was followed for AIDB installation):CREATE USER alice WITH PASSWORD '********'; GRANT CONNECT ON DATABASE <some_db> TO alice; GRANT CREATE ON SCHEMA <some_schema> TO alice; GRANT aidb_users TO alice;
Grant role access (the workaround)
To allow the user to view and query PD-created knowledge bases, grant them membership in the
visual_pipeline_userrole:GRANT visual_pipeline_user TO alice;
Configure
Update the GenAI Builder agent configuration to use the
alicecredentials (username and password) you set.
Editing external inference service parameters returns a name change error
Description: When attempting to edit the parameters of an existing external inference service, the HM console returns an error stating invalid patch inference service request: change model cluster name is not yet supported. This error occurs even if you don't attempt to change the name field. While the core functionality of the inference service remains operational, the API currently prevents updates to any configuration parameters for external models.
Workaround: To update the parameters of an external inference service, you must delete the existing service and create a new one with the desired configurations. This issue specifically affects external model services and doesn't impact internal inference services.
Missing validation message for invalid external model names
Description: When registering a new external inference service in the HM console, the system doesn't display a specific validation error message if the external service name or model name contains invalid characters. Instead, the registration page remains active without feedback, while the underlying request fails with a 400 error.
To be valid, both names must:
Consist only of lowercase alphanumeric characters, hyphens (
-), or dots (.).Start and end with an alphanumeric character.
Workaround: Ensure that all names provided during registration strictly follow the character requirements. If the page appears to hang after register an external service, verify that your service and model names don't contain uppercase letters or unsupported special characters.
Analytics and tiered tables
Updating tiered, partitioned tables fails with PGAA error
Tip
Resolved in HM versions 2026.02 and later.
Description: When attempting to execute an UPDATE statement on a large, tiered and partitioned table, the operation fails with the message ERROR: system columns are not supported by PGAA scan. This issue occurs even when the target partition for the update uses a standard heap access method (that is, it isn't an actively tiered Iceberg table), indicating a conflict in how the Analytics Accelerator (PGAA) processes the partitioned table structure during a modification query.
Table offloading fails with a 500 timeout error
Description: When attempting to offload a table to object storage, the API may return a 500 error with the message error offloading table: callback error: runner error: timeout: context deadline exceeded. This occurs when the operation takes longer than the allowed timeout period, typically due to slow write performance or high latency from the cloud provider's object storage.
Workaround: This issue is generally caused by external infrastructure bottlenecks rather than the HM deployment itself. To mitigate this, troubleshoot any performance bottlenecks or latency issues within your cloud provider's object storage service.
Once the storage performance is restored, retry the table offload operation from the HM console.
HM console and observability
False positive backup alerts for Advanced High Availability and Distributed High Availability (PGD) clusters
Tip
Resolved in HM versions 2026.02 and later.
Description: Backup-related alerts, specifically pem_time_since_last_backup_available_seconds and pem_backup_longer_than_expected, can trigger false positives for Advanced High Availability and Distributed High Availability (PGD) clusters. This occurs because these alerts currently target individual pods rather than the cluster as a whole. In a data group with multiple nodes, backups are typically executed on only one node. Consequently, the other nodes incorrectly trigger alerts for missing or delayed backups.
Workaround: To avoid unnecessary notifications in the HM console, you can silence these specific alerts for your Advanced High Availability and Distributed High Availability (PGD) clusters using one of the following methods:
HM console: In your project, navigate to Settings > Alerts and silence
pem_time_since_last_backup_available_secondsandpem_backup_longer_than_expected.Alertmanager: Create a silence rule for these two alerts targeting your Advanced High Availability and Distributed High Availability (PGD) environment.
HTTP 431 "Request Header Fields Too Large" error when accessing the Estate page
Description: Users who have access to a large number of projects (typically more than 50) may encounter an HTTP 431 error when navigating to the Estate page in the HM console. This error occurs because the authorization headers generated for the request exceed the size limits of the upstream proxy or load balancer. This issue prevents the HM console from loading estate results and can also affect machine users or automation scripts calling the /api/v1/estate endpoint directly.
Workaround: For users impacted by this error, an organization owner must reduce the size of the request headers by performing one of the following actions:
Revoke project access: Remove the affected user's access to projects that are no longer actively required.
Remove unused projects: Delete projects that are no longer in use to reduce the total count associated with the user's profile.
Clusters and upgrades
Major version upgrade fails for Advanced High Availability and Distributed High Availability (PGD) clusters with witness groups
Tip
Resolved in HM versions 2026.02 and later.
Description: Performing an in-place major version upgrade of the database engine (for example, from Postgres/EPAS 17 to 18) fails for Advanced high Availability and Distributed High Availability (PGD) clusters configured with two data groups and one witness group. The upgrade process becomes stuck in the "Waiting for nodes major version in-place upgrade" phase due to inactive replication slots. This results in the upgrade pod failing to progress, and the PGD CLI reporting a critical status for the cluster.
Workaround: Avoid performing an in-place major version upgrade for this specific cluster configuration. Instead, provision a new Advanced high Availability or Distributed High Availability (PGD) cluster using the target major version and use the Data Migration Service (DMS) to migrate your schema and data from the old cluster to the new one.
AI Factory
Index analysis actions fail due to missing hypopg extension
Description: The AI Factory actions analyze_workload_indexes and analyze_query_indexes are currently unavailable because the required hypopg extension is missing from the standard HM database images. Attempting to run these actions will result in an error indicating the extension is not installed.
Workaround: There is currently no manual workaround to install this extension on managed clusters. Avoid using these two specific actions until the extension is included in a future image update.
Deleted clusters still appear in AI components
Tip
Resolved in HM versions 2026.02 and later.
Description: When configuring an EDB DB Component or an EDB Knowledge Base Component (such as within Langflow), Advanced High Availability and Distributed High Availability (PGD) clusters that have already been deleted from the HM console may still appear in the selection list. Attempting to use a deleted cluster will result in an execution error.
Workaround: Before selecting a cluster in the AI components, verify its status in the HM console or via the clusters API. Ensure you only select clusters that are currently in a "Healthy" or "Active" state.
Missing validation for required MCP tool parameters
Description: Several actions within the MCP tools allow fields to be left empty during configuration, which results in execution errors rather than validation warnings. If these parameters are not populated, the workflow may fail to build or return an "Unsupported object type" error.
Affected actions and parameters:
list_objectsandget_object_details: The Object Type field must not be empty.explain_query: The Analyze andhypothetical_indexesfields must be populated with specific data types.
Workaround: Ensure the following parameters are manually filled before executing the flow:
list_objects(Object Type): Entertable,view,sequence,function,stored procedure, orextension.get_object_details(Object Type): Entertable,view,sequence, orextension.explain_query(Analyze): EnterTrueorFalse.explain_query(hypothetical_indexes): Use tool mode to provide a valid list.
Advanced high Availability and Distributed High Availability (PGD) witness groups appear in database selection lists
Tip
Resolved in HM versions 2026.02 and later.
Description: When using the EDB Database Component or EDB Knowledge Base Component with a Advanced High Availability and Distributed High Availability (PGD) cluster, the witness group is incorrectly included in the list of available database groups. Because witness groups don't contain actual database data or connection strings, selecting one will result in a failure to connect or display information.
Workaround: When configuring these components, manually ignore any entries labeled as a witness group. Only select data groups to ensure a valid connection and successful data retrieval.
Text search may match on non-visible fields
Description: When using the search functionality in the HM console, for example in the Activity Log section, the system performs a full-text search across all underlying data fields. As a result, search results may include resources or activity log entries where the visible Activity Name or other shown attributes don't appear to match the search term.
Workaround: There is currently no workaround for this behavior as it is a result of the underlying search design. Users should be aware that search results are inclusive of internal action details not displayed in the primary log view.
Migrations
Known issues pertaining to the HM Migration Portal, data migration workflows, and schema ingestion workflows are maintained on a dedicated page in the Migrating databases documentation. See Known issues, limitations, and notes for a complete list.