Configuring
Implementing Imperva Data Security Fabric with EDB Postgres Advanced Server and PostgreSQL requires the following components:
- Imperva Agent
- Imperva Database Security Gateway
- Imperva Management Server
- EDB Postgres Advanced Server or PostgreSQL
Prerequisites
- A running Imperva Data Security Fabric environment
- Imperva Gateway registered to the Imperva Management server
- Imperva Agent installed on the EDB database
- Imperva Agent registered to the Imperva Gateway
Configure Imperva Data Security Fabric for EDB Postgres Advanced Server
Configure the Imperva Data Security Fabric Agent so you can use it to help monitor your EDB Postgres Advanced Server database or your PostgreSQL database.
Basic Imperva Data Security Fabric configuration overview
The primary objective of the basic configuration is to identify the traffic you want to protect. You can accomplish this objective by defining the basic building blocks that comprise the Imperva Data Security Fabric domain. To do so, you use several parameters, including IP addresses, ports, protocols, and more. The screen shots show basic configurations of these components.
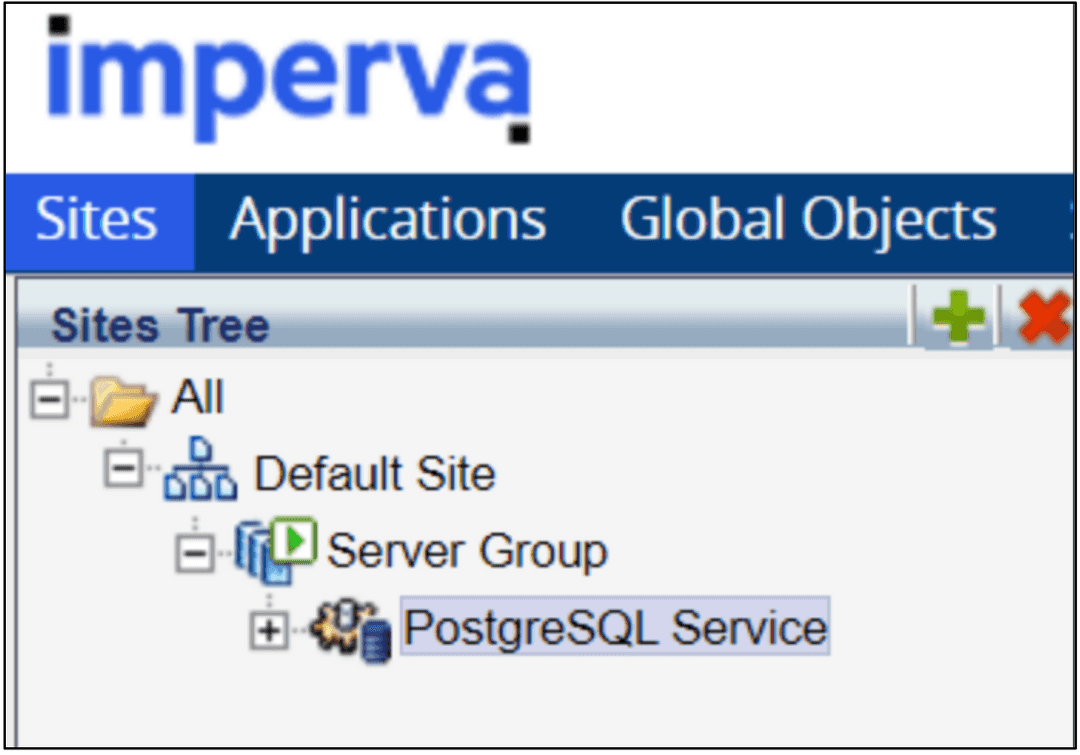
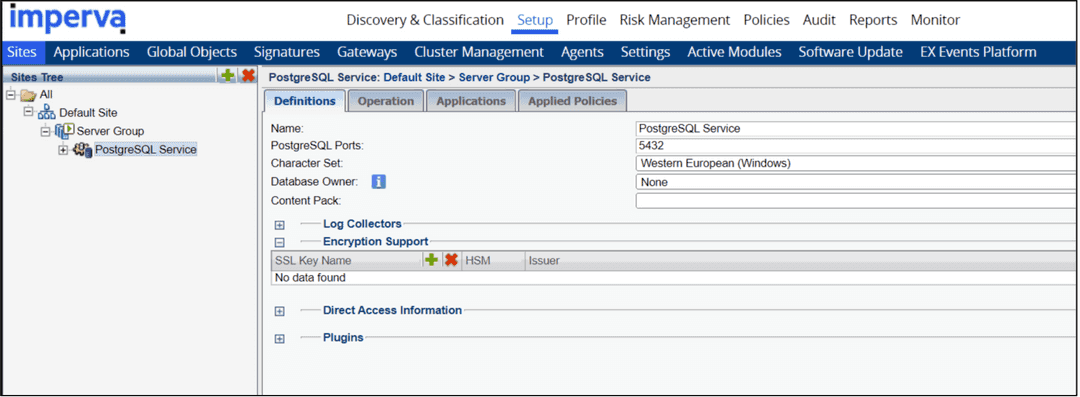
You can take several configuration steps with the Imperva Data Security Fabric Agent in your environment, as it's a highly configurable agent. These configuration steps provide custom protection and support for your EDB Postgres Advanced Server and PostgreSQL databases. For a complete list of configuration options, see the Basic Imperva Data Security Fabric configuration documentation.
Configure the basic components in the following order:
Sites: The primary container of all other objects.
Server groups: One or more servers at a specific location based on IP addresses. To create and manage server groups, see Basic Server Group Configuration in the Imperva documentation.
Services: A service type hosted by a server group based on service. Represents a database service, for example, PostgreSQL database. Inside a server group can be a number of services on different ports and various database types.
Application: Represents one or more databases and schemas operating on a database service. For example, inside a single PostgreSQL database server installation, two databases can be running. By assigning to different database applications, you can assign different policies to protect each database.
Could this page be better? Report a problem or suggest an addition!