Configuration
Implementing EDB Postgres for Kubernetes with Kasten by Veeam requires the following components:
Prerequisites
- EDB Postgres for Kubernetes configured and running
- EDB Postgres for Kubernetes external backup adapter configured per your system requirements
- Kasten K10 installed on your system
Note
For this integration, use the example.yaml files provided for the appropriate Kasten configuration pieces, and change any environment variables per your specific needs.
See Add the backup decorator annotations to the cluster, which is important for the Kasten add-on integration.
Refer to the EDB Postgres for Kubernetes external backup adapter documentation for more detailed information on the EDB Postgres for Kubernetes backup adaptor add-on functionality and additional details on its configuraton parameters.
Install the operator
Install the EDB Postgres for Kubernetes operator.
kubectl apply -f https://get.enterprisedb.io/cnp/postgresql-operator-1.20.2.yamlRunning this command creates the operator namespace where the controller runs.
Create an EDB cluster and client and add data
- In your Kubernetes environment, create a specific namespace and apply your
.yamlfile:
kubctl create ns edb kubectl apply -f cluster-example.yaml -n edb
Example cluster-example.yaml file:
# Example of PostgreSQL cluster apiVersion: postgresql.k8s.enterprisedb.io/v1 kind: Cluster metadata: name: cluster-example annotations: "k8s.enterprisedb.io/addons": '["kasten"]' spec: instances: 3 # Example of rolling update strategy: # - unsupervised: automated update of the primary once all # replicas have been upgraded (default) # - supervised: requires manual supervision to perform # the switchover of the primary primaryUpdateStrategy: unsupervised # Require 1Gi of space storage: size: 1Gi
- Wait until the cluster is completely ready.
kubectl get clusters.postgresql.k8s.enterprisedb.io -n edb NAME AGE INSTANCES READY STATUS PRIMARY cluster-example 19m 3 3 Cluster in healthy state cluster-example-1
- Install the cnp plugin.
curl -sSfL \ https://github.com/EnterpriseDB/kubectl-cnp/raw/main/install.sh | \ sudo sh -s -- -b /usr/local/bin
- Create a client certificate to the database.
kubectl cnp certificate cluster-app \ --cnp-cluster cluster-example \ --cnp-user app \ -n edb
- Create the client.
kubectl create -f client.yaml -n edb
Example client.yaml file:
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: cert-test spec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: app: webtest template: metadata: labels: app: webtest spec: containers: - image: ghcr.io/cloudnative-pg/webtest:1.6.0 name: cert-test volumeMounts: - name: secret-volume-root-ca mountPath: /etc/secrets/ca - name: secret-volume-app mountPath: /etc/secrets/app ports: - containerPort: 8080 env: - name: PGPASSWORD valueFrom: secretKeyRef: name: cluster-example-app key: password - name: DATABASE_URL value: > sslkey=/etc/secrets/app/tls.key sslcert=/etc/secrets/app/tls.crt sslrootcert=/etc/secrets/ca/ca.crt host=cluster-example-rw.default.svc dbname=app user=app sslmode=verify-full - name: SQL_QUERY value: SELECT 1 volumes: - name: secret-volume-root-ca secret: secretName: cluster-example-ca defaultMode: 0600 - name: secret-volume-app secret: secretName: cluster-app defaultMode: 0600
- Add some data into the cluster to test the backup and restore. The following is sample data that was used for this example:
kubectl exec -it deploy/cert-test -- bash psql 'sslkey=/etc/secrets/app/tls.key sslcert=/etc/secrets/app/tls.crt sslrootcert=/etc/secrets/ca/ca.crt host=cluster-example-rw dbname=app user=app sslmode=verify-full' \c app DROP TABLE IF EXISTS links; CREATE TABLE links ( id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY, url VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, description VARCHAR (255), last_update DATE ); INSERT INTO links (url, name, description, last_update) VALUES('https://kasten.io','Kasten','Backup on kubernetes',NOW()); select * from links; \q exit
Add the backup decorator annotations to the cluster
If you created the cluster from the previous process, cluster-example.yaml already includes the Kasten add-on, and you can skip this part. If you're working with your own cluster, you need to add the Kasten add-on.
- Add the following annotations to your cluster. The previous
cluster-example.yamlfile shows an example of where to add the annotation.
"k8s.enterprisedb.io/addons": '["kasten"]'
Install the EDB blueprint
- In your environment, enter:
kubectl create -f edb-hooks.yamlExample edb-hooks.yaml file:
apiVersion: cr.kanister.io/v1alpha1
kind: Blueprint
metadata:
name: edb-hooks
namespace: kasten-io
actions:
backupPrehook:
phases:
- func: KubeTask
name: edbPreBackupHook
args:
image: ghcr.io/kanisterio/kanister-kubectl-1.18:0.91.0
command:
- bash
- -x
- -o
- errexit
- -o
- pipefail
- -c
- |
namespace={{ .Namespace.Name }}
selector='kasten-enterprisedb.io/hasHooks=true'
for pod in $(kubectl get po --no-headers -n $namespace -l $selector|awk '{print $1}')
do
preCommand=$(kubectl get po -n $namespace $pod -o jsonpath='{.metadata.annotations.kasten-enterprisedb\.io/pre-backup-command}')
preOnErrorCommand=$(kubectl get po -n $namespace $pod -o jsonpath='{.metadata.annotations.kasten-enterprisedb\.io/pre-backup-on-error}')
container=$(kubectl get po -n $namespace $pod -o jsonpath='{.metadata.annotations.kasten-enterprisedb\.io/pre-backup-container}')
command=${preCommand//[\[\]\"\,]/' '}
result=$(kubectl exec -it $pod -c $container -n $namespace $pod -- bash -c "if $command; then echo success; else echo failure; fi" | tail -1)
if [[ $result == "failure" ]]
then
echo "Error after running $preCommand in $pod/$container"
echo "Executing $preOnErrorCommand"
command=${preOnErrorCommand//[\[\]\"\,]/' '}
kubectl exec -it $pod -c $container -n $namespace $pod -- bash -c $command
exit 1
fi
done
exit 0
backupPosthook:
phases:
- func: KubeTask
name: edbPostBackupHook
args:
image: ghcr.io/kanisterio/kanister-kubectl-1.18:0.91.0
command:
- bash
- -x
- -o
- errexit
- -o
- pipefail
- -c
- |
namespace={{ .Namespace.Name }}
selector='kasten-enterprisedb.io/hasHooks=true'
for pod in $(kubectl get po --no-headers -n $namespace -l $selector|awk '{print $1}')
do
postCommand=$(kubectl get po -n $namespace $pod -o jsonpath='{.metadata.annotations.kasten-enterprisedb\.io/post-backup-command}')
container=$(kubectl get po -n $namespace $pod -o jsonpath='{.metadata.annotations.kasten-enterprisedb\.io/post-backup-container}')
command=${postCommand//[\[\]\"\,]/' '}
result=$(kubectl exec -it $pod -c $container -n $namespace $pod -- bash -c "if $command; then echo success; else echo failure; fi" | tail -1)
if [[ $result == "failure" ]]
then
echo "Error after running $postCommand in $pod/$container"
exit 1
fi
done
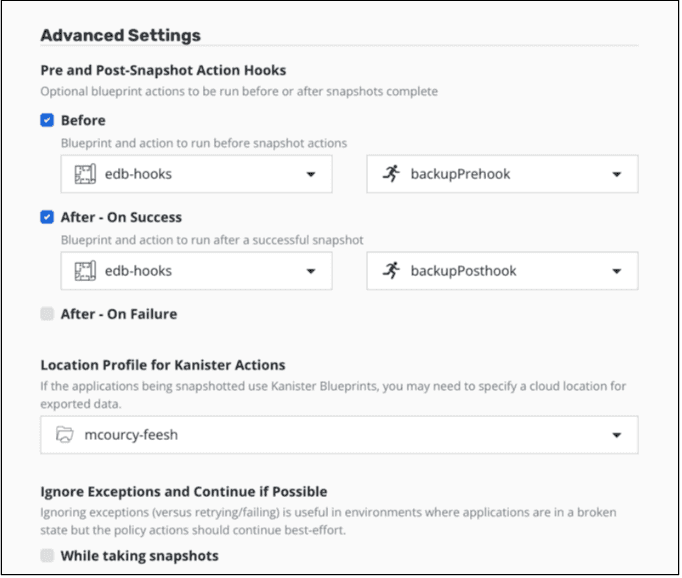
exit 0Create a backup policy with the EDB hooks
Launch the Kasten K10 interface.
Create a policy for the EDB namespace. You need to set up a location profile for the export and kanister actions.
Add the hooks example:
Could this page be better? Report a problem or suggest an addition!