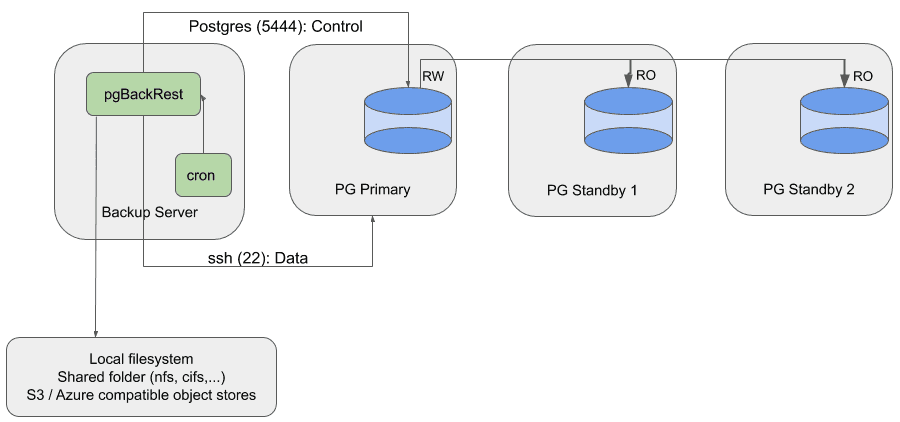
Use Case 2: Running pgBackRest from a Dedicated Repository Host
Description
- pgBackRest runs on a dedicated backup server and stores repository on local or remote storage (NFS, SFTP, S3, Azure or GCS compatible object stores).
- Cron task active to take backups from the primary database cluster.
- Manually reconfigure cron task to take backup from another server.
Create a Dedicated User on the Repository Host
The pgbackrest user is created to own the backups and archives repository. Any user can own the repository, but it is recommended not to use postgres or enterprisedb to avoid confusion.
$ sudo groupadd pgbackrest $ sudo adduser -g pgbackrest -n pgbackrest $ sudo chown pgbackrest: /var/log/pgbackrest
Setup Passwordless SSH Connection
pgBackRest requires a passwordless SSH connection to enable communication between the hosts.
The following example SSH commands should succeed without prompting you for a password:
# From the PostgreSQL nodes $ sudo -u postgres ssh pgbackrest@backup-server # From the EDB Postgres Advanced Server nodes $ sudo -u enterprisedb ssh pgbackrest@backup-server # From the repository host $ sudo -u pgbackrest ssh postgres@postgres-node-1 $ sudo -u pgbackrest ssh postgres@postgres-node-2 $ ...
Configuration
Backup Server
The repository should be reachable from the backup server. It can be located on the various supported types described in the first use case.
For example, let us create /backup_space to store our backups and archives locally:
$ sudo mkdir /backup_space $ sudo chown pgbackrest: /backup_space
The [global] section of the configuration file will look like this:
[global] repo1-path=/backup_space repo1-retention-full=2 repo1-cipher-type=aes-256-cbc repo1-cipher-pass=FIXME process-max=FIXME log-level-console=info log-level-file=debug start-fast=y delta=y
Adjust the encryption passphrase and the maximum number of processes to use for compression usage and file transfer.
See the Recommended settings pages for more details.
The [demo] stanza section will contain specific pg- options for each database node.
- the primary database server configuration for PostgreSQL
pg1-host=postgres-node-1 pg1-path=/var/lib/pgsql/13/data
or for EDB Postgres Advanced Server
pg1-host=postgres-node-1 pg1-host-user=enterprisedb pg1-path=/var/lib/edb/as13/data
- for every other PostgreSQL node
pg2-host=other_node_hostname_or_ip pg2-path=/var/lib/pgsql/13/data
or for EDB Postgres Advanced Server
pg2-host=other_node_hostname_or_ip pg2-host-user=enterprisedb pg2-path=/var/lib/edb/as13/data
Define multiple nodes using pg2, pg3,... to reach standby servers only when those servers are available.
Database server(s)
Update the pgBackRest configuration file on the database server(s):
# pgbackrest.conf [global] repo1-host=backup-server repo1-host-user=pgbackrest log-level-console=info log-level-file=debug delta=y [demo] pg1-path=/var/lib/pgsql/13/data recovery-option=primary_conninfo=host=primary_vip user=replication_user ...
The [demo] stanza section will be different for PostgreSQL or for EDB Postgres Advanced Server, and the recovery-option is used to set the replication primary_conninfo after executing the restore command. For more details, please refer to the Use case 1 page for more details.
Setup Archiving
Once pgBackRest is configured, set up the database archiver process on each node:
# postgresql.conf archive_mode = on archive_command = 'pgbackrest --stanza=demo archive-push %p'
As changing the archive_mode parameter requires a service restart, and changing the archive_command only requires a configuration reload, we recommend enabling archive_mode with an empty archive_command (or pointing to /bin/true) when initiating a new database cluster.
From the backup server (also called repository host), initiate the pgBackRest repository with the system user we created earlier:
$ sudo -u pgbackrest pgbackrest --stanza=demo stanza-create
Check the configuration and the archiving process:
$ sudo -u pgbackrest pgbackrest --stanza=demo check
Backup and Restore
See the Quick start backups and restore sections for more details about those two commands.
The backup command will be executed on the repository host (aka. backup-server), while the restore command should be executed on database nodes (aka. postgres-node-1,...).
Glossary
pgBackRest
delta
log-level-console
log-level-file
pg-host
pg-path
pg-port
pg-user
process-max
recovery-option
repo-cipher-pass
repo-cipher-type
repo-host
repo-host-user
repo-path
repo-retention-full
start-fast
PostgreSQL
Could this page be better? Report a problem or suggest an addition!